INDUSTRY SECTORS
LIFE SCIENCES
Peptides Synthesis
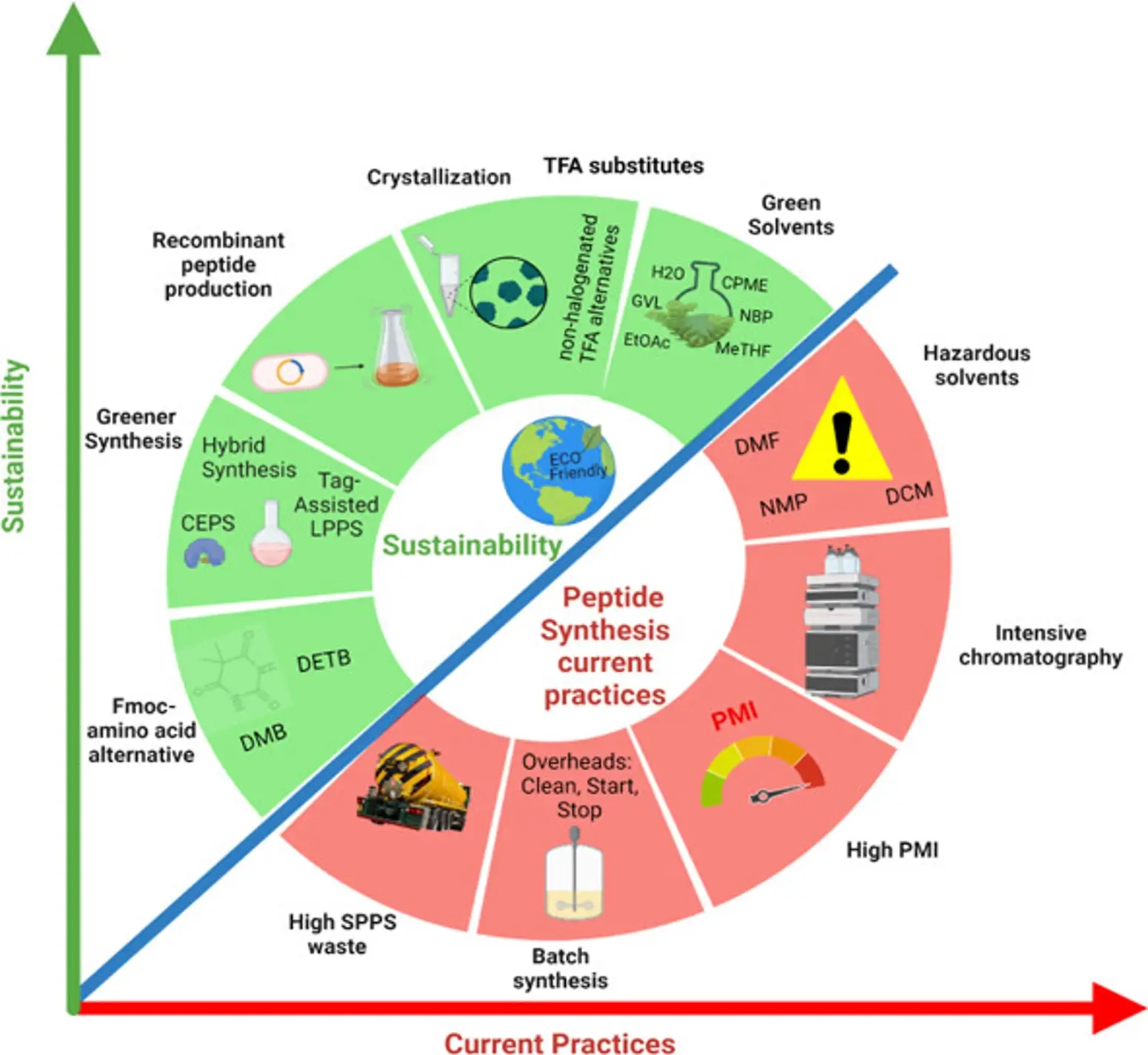
In Pharmaceutical Industry, therapeutic peptides like GLP have been instrumental in providing solutions to challenges that traditional small molecules often cannot address. Solid Phase Peptide synthesis (SPPS) is the most widely used process for the production of peptides. SPPS often involves use of organic solvents in both synthesis and purification steps, generating significant waste and consuming vast resources.
ICN offers sustainable solutions using Green Chemistry & Green Engineering principles which aid in waste reduction and energy conservation. ICN Technologies lead to considerable decrease in Process Mass (Solvent) Intensity, PMI, by about 85-95%.
Challenges in Current Practices
- High Solvent Consumption; High OPEX
- Peptide Degradation during Concentration
- High CAPEX and OPEX of Lyophilizer due to
- High Residual Solvents in product
- Low Concentration of Product in HPLC Eluent
Average Process Mass Intensity (PMI) per AA (Amino Acid), for peptide production by SPPS – 874.5
(including water), 489.7 (Solvent only)- (as per data for 14 Commercial and Phase 3 Peptides)
Process Solvent Intensity for Semaglutide – 15181 (31 AA)
Source: J. Org. Chem. 2024, 89, 7, 4261-4282
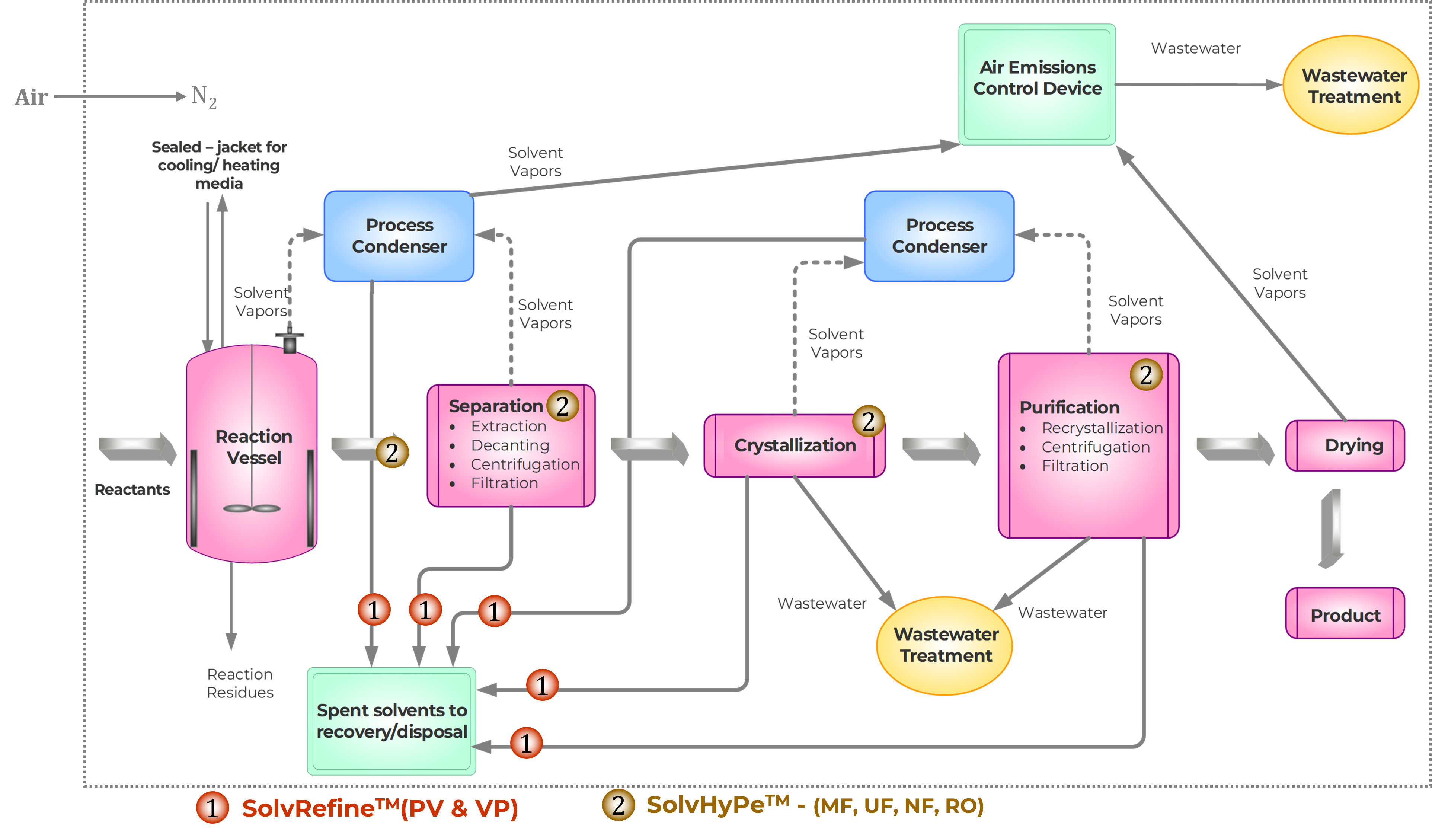
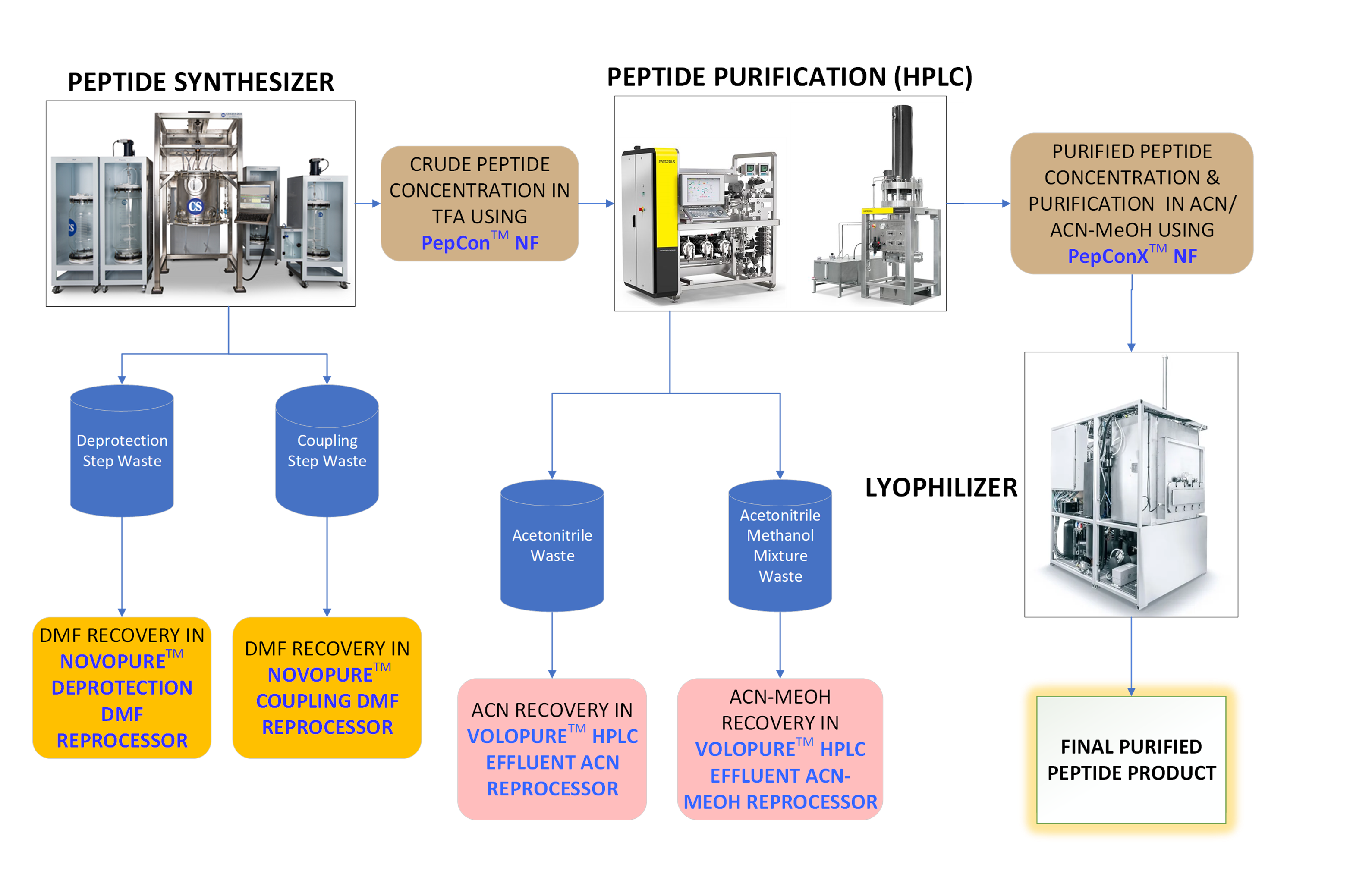
MolSep™ Opportunities in SPPS
Source :
CSBio Automated Commercial Scale Peptide Synthesizer (CSBio – Automated Peptide Synthesizers and Oligo Synthesizers)
Sartorius HPLC Flowdrive and Column (HPLC Systems | Sartorius)
SP Hull LyoConstellation S10/S20/S30 Pilot Lyophilizers (Hull LyoConstellation S10/S20/S30 Pilot Lyophilizers – Scientific Products)
Reprocessing of Dimethylformamide from Synthesis steps – The system recovers dimethylformamide (DMF) waste generated from deprotection & coupling steps and returns the DMF at a level of purity that can be reused in the peptide manufacturing process. This Significantly reduces the DMF consumption and waste generation while maintaining high product purity.
Reprocessing of waste Acetonitrile from HPLC Purification step – The system recovers chromatography solvent, Acetonitrile and returns it at a level of purity that can be reused in the peptide manufacturing process. This significantly reduces solvent consumption and waste generation while maintaining high product purity.
Concentration of crude peptide in TFA – The system concentrates Crude Peptide in Trifluoroacetic Acid (TFA) using solvent stable nanofiltration membranes. It operates at low temperatures and eliminates the risk of Peptide degradation during concentration.
Concentration & Purification of Peptide – The system concentrates Peptide and removes residual solvents by Diafiltration. Residual Solvent concentration in the final product is reduced to the limit acceptable as per ICH guidelines. It operates at low temperatures and eliminates the risk of Peptide degradation during concentration. Our technology reduces the CAPEX and OPEX requirements for Lyophilizer.
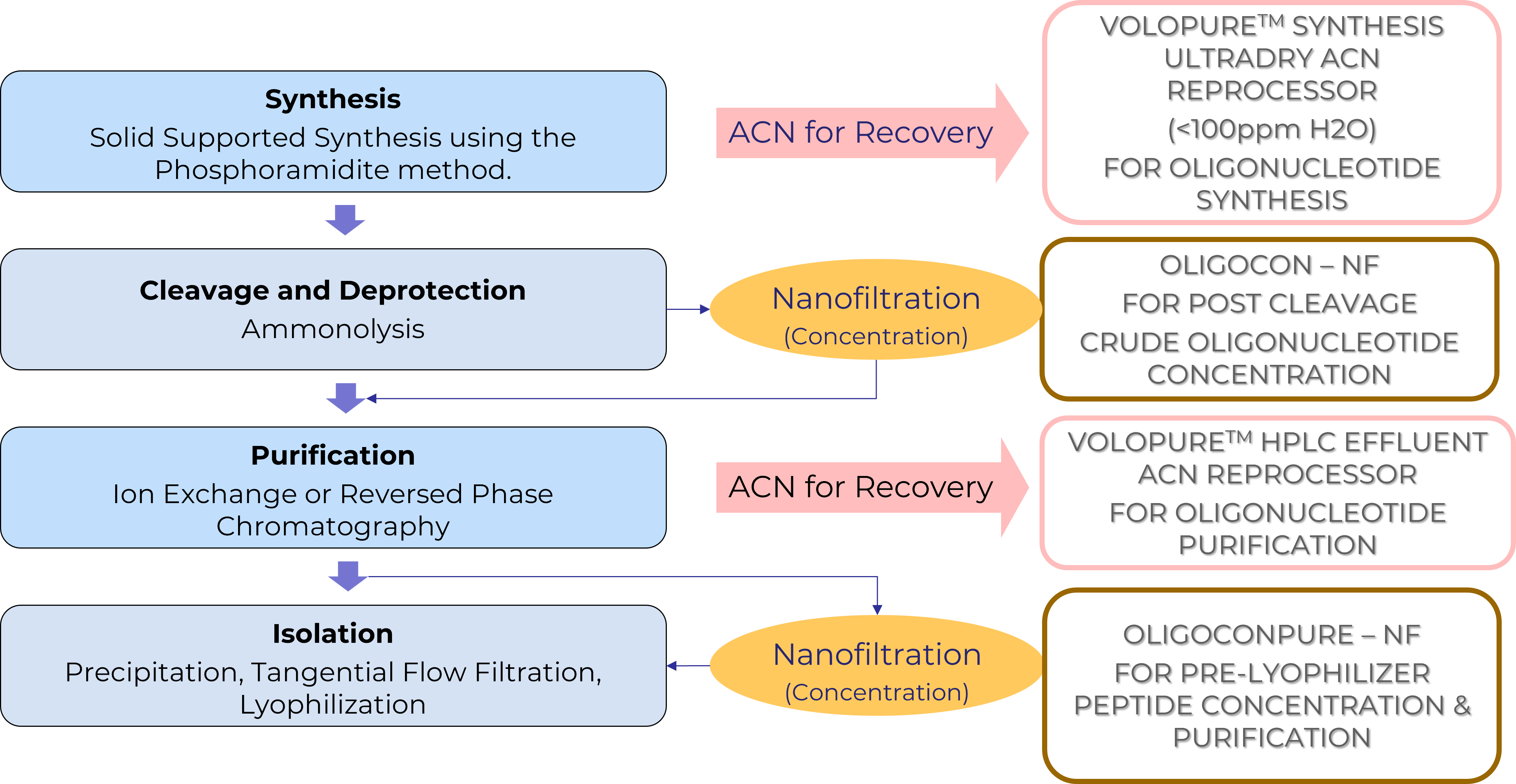
Oligonucleotide Synthesis
Just like peptides, there’s a growing interest in Therapeutic oligonucleotides in Pharmaceuticals. In making the solid phase production process more sustainable, there are challenges imposed by use of large volumes of hazardous reagents and solvents during synthesis and purification.
ICN offers sustainable solutions using Green Chemistry & Green Engineering principles that aid in waste reduction and energy conservation.
MolSep™ Opportunities in Solid Phase Oligonucleotide Synthesis
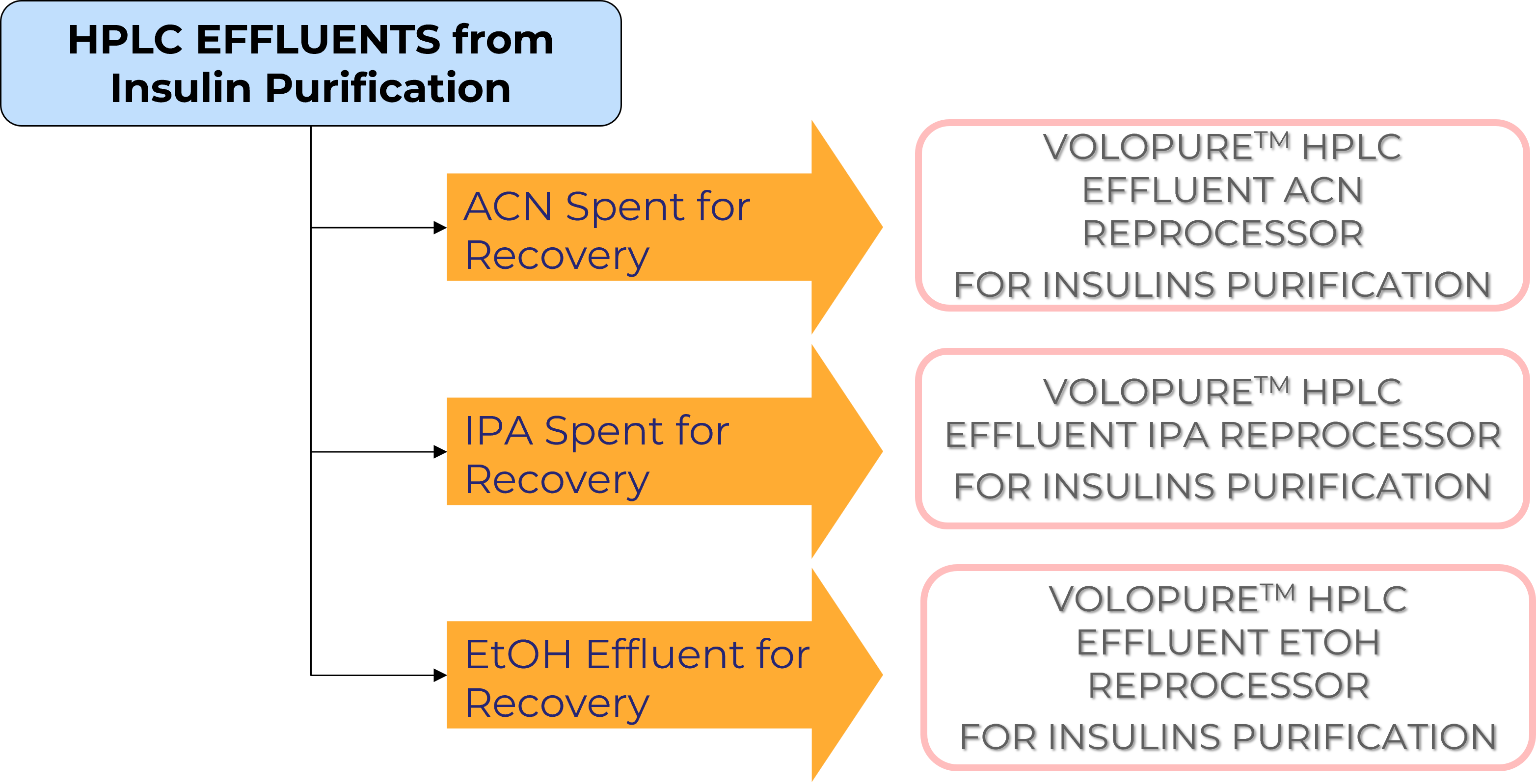
Insulins and Insulin Biosimilars Production
MolSep™ Opportunities in Insulins and Insulin Biosimilars Production
SolvHyPe™ and AquaHyPe Systems can be applied for concentration and/or diafiltration of the product stream prior to HPLC or post HPLC (prior to lyophilization) or both, as required.
Small Molecule APIs Synthesis
Life Sciences sector uses organic solvents for chemical processes (e.g. synthesis, precipitation) and other operations including drying, cleaning etc. These solvents often become contaminated with water as a result of their use.
Water source(s) can be:
- By product in the reaction
- From raw materials
- From washes/extraction
- Ingress from Atmosphere
Why do we need to remove water in some chemical reactions?
- In a reversible reaction where water is a byproduct, water extraction is required to drive the reaction forward (common e.g. – ester synthesis)
- Water may react with the reactants to form side products and thereby decrease yield.
- Presence of water may possibly result in change in polymorph structure of the desired product.
- In certain reactions, water may react with certain reagents and reaction may get inhibited (common e.g. – synthesis using Grignard’s Reagent where water can rapidly destroy the reagent). Some of the moisture sensitive compounds are as below:
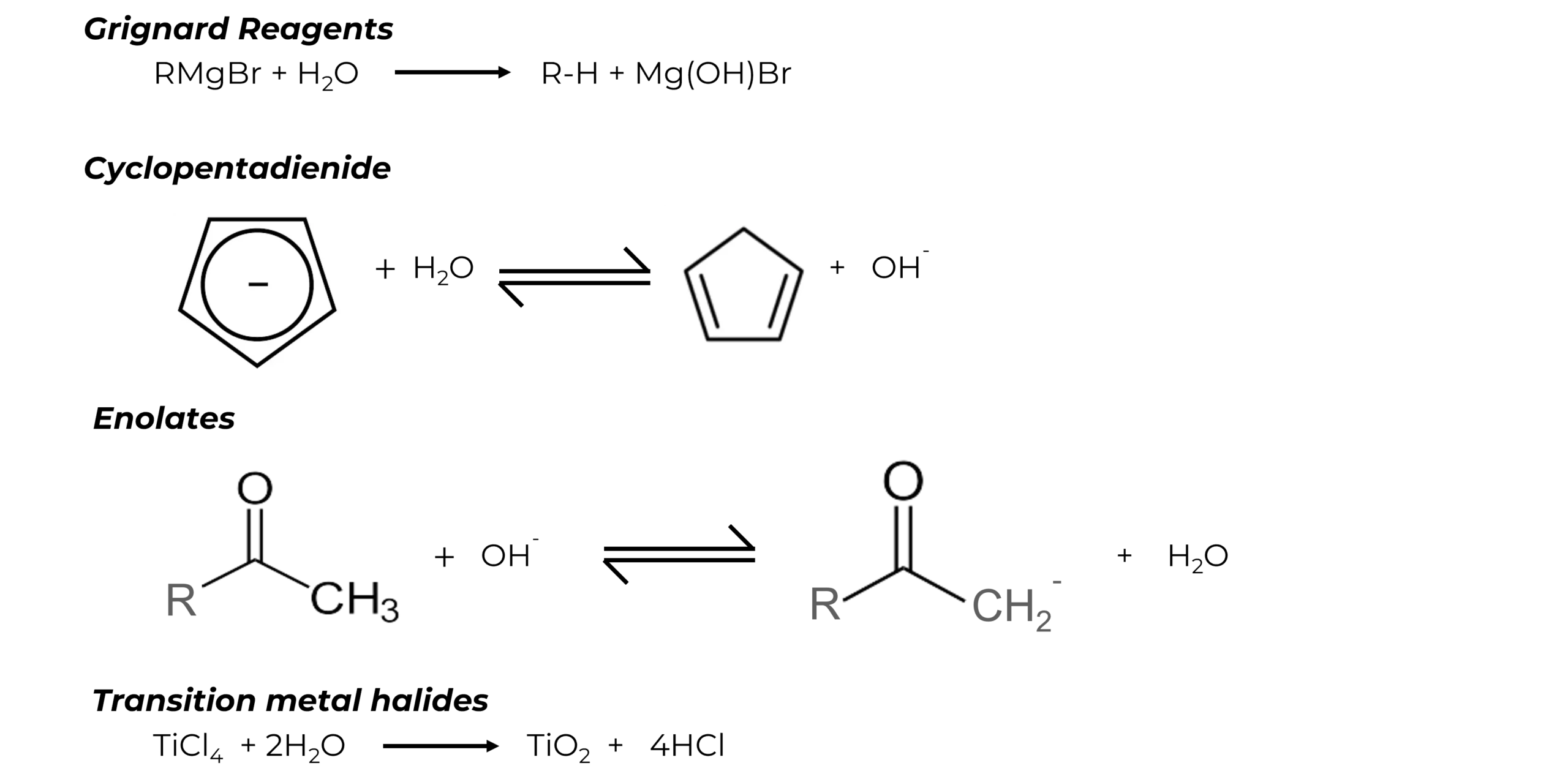
Since the cost of purchasing virgin solvents is continuously increasing and the disposal of spent is becoming expensive, the economics of recovery of solvents from spent liquid or air streams are very compelling.
SolvHyPe™ has following applications in this industry:
- SolChase – Solvent exchange for crystallizing the product, or simply for the next reaction step in a telescopic work-up
- ProdCon – Concentration of residual API in the mother liquor after crystallization for increased yield.
- ProdCon – Concentration of product in preparative HPLC product fraction for product recovery
- ProdPure – Impurity concentration in preparative HPLC waste fraction for waste volume reduction
- ProdPure – Removal of chromophores from product (in many cases, need for carbon treatment is obviated or at least reduced)
Refer Illustration for ICN Applications in the process.
MolSep™ Opportunities in Small Molecule Synthesis (Chemical Route)